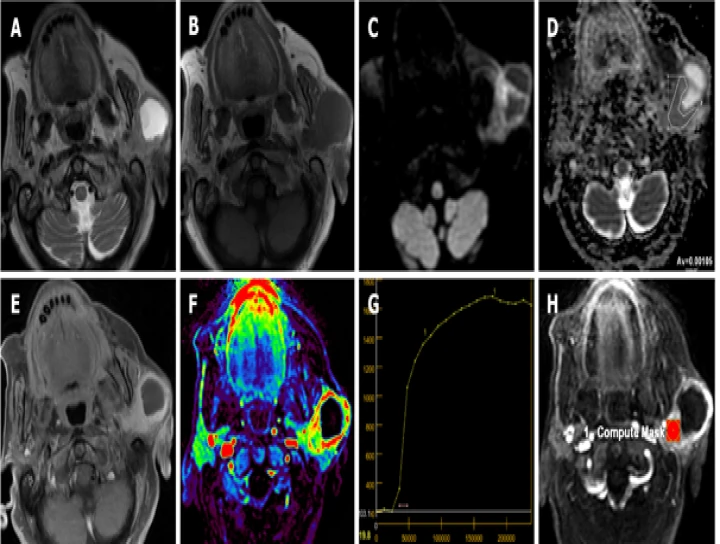
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) plays a crucial role in the evaluation of buccal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), particularly in assessing its extent and involvement of adjacent structures such as the salivary glands. Here's a breakdown of how MRI is used to evaluate salivary gland involvement by buccal SCC:
1. **High-resolution Imaging**: MRI provides detailed images of the soft tissues, allowing for precise delineation of tumor margins and assessment of invasion into surrounding structures, including the salivary glands. High-resolution sequences such as T1-weighted, T2-weighted, and contrast-enhanced sequences are commonly used to visualize the extent of the tumor and its relationship to nearby structures.
2. **Multiplanar Imaging**: MRI allows imaging in multiple planes (axial, coronal, and sagittal), enabling comprehensive assessment of tumor spread and its proximity to the salivary glands from various perspectives. This multiplanar capability is particularly valuable in evaluating the complex anatomy of the head and neck region.
3. **Contrast Enhancement**: Intravenous contrast administration during MRI enhances the visualization of tumor vascularity and highlights areas of enhancement, aiding in the differentiation between tumor tissue and normal structures. Contrast-enhanced MRI can help identify regions of salivary gland involvement by buccal SCC, as areas of abnormal enhancement may indicate tumor infiltration.
4. **Functional Imaging**: Advanced MRI techniques such as diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) offer functional information about tissue cellularity, metabolism, and microstructure. These techniques can help characterize the biological behavior of the tumor and assess its aggressiveness, which may influence treatment planning and prognosis.
5. **Assessment of Lymph Node Involvement**: MRI is also valuable in evaluating regional lymph nodes for metastatic spread from buccal SCC. Enlarged or suspicious lymph nodes can be identified on MRI, and their relationship to the primary tumor and nearby salivary glands can be assessed, aiding in staging and treatment decisions.
Overall, MRI is an indispensable tool in the comprehensive evaluation of buccal SCC, providing detailed anatomical and functional information that aids in the assessment of salivary gland involvement, tumor extent, and treatment planning. Close collaboration between radiologists, oncologists, and surgeons is essential for optimal patient management based on MRI findings.


No Any Replies to “MRI EVALUATION OF SALIVARY GLAND INVOLVEMENT BY BUCCAL SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA”
Leave a Reply