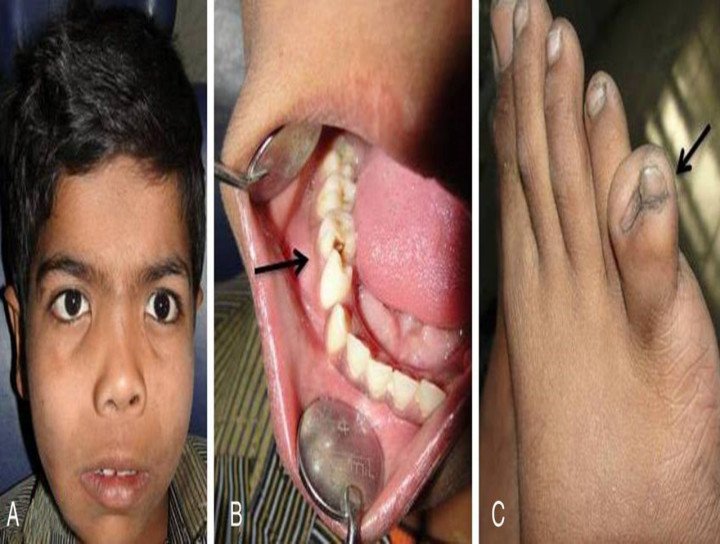
Gorlin Goltz Syndrome also known as Nevoid basal-cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS), is an inherited medical condition involving defects within multiple body systems such as the skin, nervous system, eyes, endocrine system, and bones. People with this syndrome are particularly prone to developing a common and usually non-life-threatening form of non-melanoma skin cancer. About 10% of people with the condition do not develop basal-cell carcinomas (BCCs). NBCCS is an autosomal dominant condition that can cause unusual facial appearances and a predisposition for basal-cell carcinoma, a type of skin cancer which rarely spreads to other parts of the body. The prevalence is reported to be 1 case per 56,000–164,000 population. Recent work in molecular genetics has shown NBCCS to be caused by mutations in the PTCH (Patched) gene found on chromosome arm 9q. If a child inherits the defective gene from either parent, he or she will have the disorder.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Multiple basal-cell carcinomas of the skin, Odontogenic keratocyst, Rib and vertebrae anomalies, Intracranial calcification, skeletal abnormalities like bifid ribs, kyphoscoliosis, early calcification of falx cerebri, Distinct faces: frontal and temporoparietal bossing, hypertelorism, and mandibular prognathism, Bilateral ovarian fibromas, 10% develop cardiac fibromas.
CAUSE
Mutations in the human homologue of Drosophila patched (PTCH1), a tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 9, were identified as the underlying genetic event in this syndrome.
DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosis of NBCCS is made by having 2 major criteria or 1 major and 2 minor criteria.
The major criteria consist of the following:
1. More than 2 BCCs or 1 BCC in a person younger than 20 years;
2. Odontogenic keratocysts of the jaw
3. 3 or more palmar or plantar pits
4. Ectopic calcification or early (<20 years) calcification of the falx cerebri
5. Bifid, fused, or splayed ribs
6. First-degree relative with NBCCS.
The minor criteria include the following:
1. Macrocephaly.
2. Congenital malformations, such as cleft lip or palate, frontal bossing, eye anomaly (cataract, coloboma, microphthalmia, nystagmus).
3. Other skeletal abnormalities, such as Sprengel deformity, pectus deformity, polydactyly, syndactyly or hypertelorism.
4. Radiologic abnormalities, such as bridging of the sella turcica, vertebral anomalies, modeling defects or flame-shaped lucencies of hands and feet.
5. Ovarian and cardio fibroma or medulloblastoma
CONCLUSION
People with NBCCS need education about the syndrome, and may need counseling and support, as coping with the multiple BCCs and multiple surgeries is often difficult. They should reduce UV light exposure, to minimize the risk of BCCs. They should also be advised that receiving Radiation therapy for their skin cancers may be contraindicated. They should look for symptoms referable to other potentially involved systems: the CNS, the genitourinary system, the cardiovascular system, and dentition.


No Any Replies to “GORLIN GOLTZ SYNDROME: AN ENIGMA”
Leave a Reply