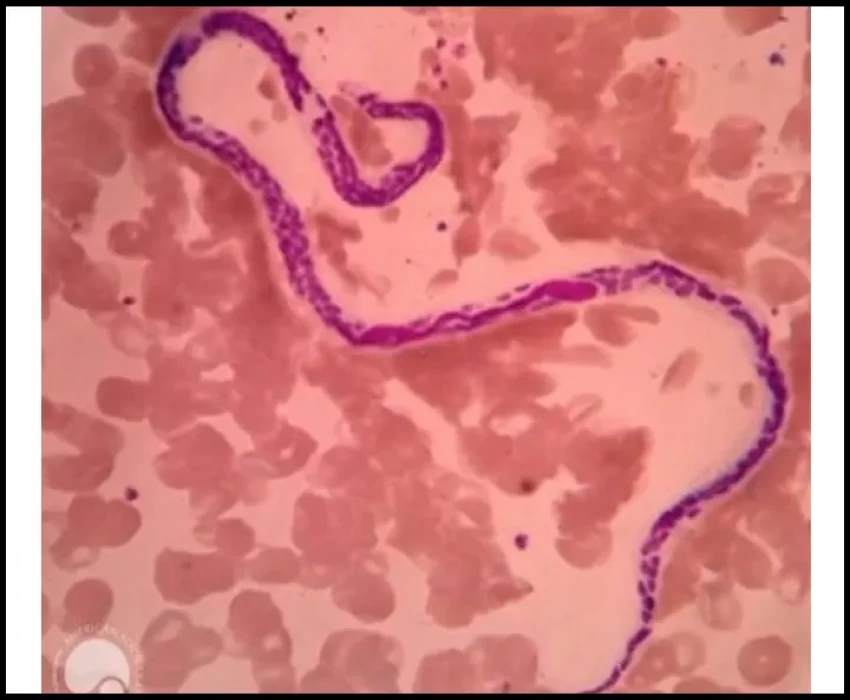
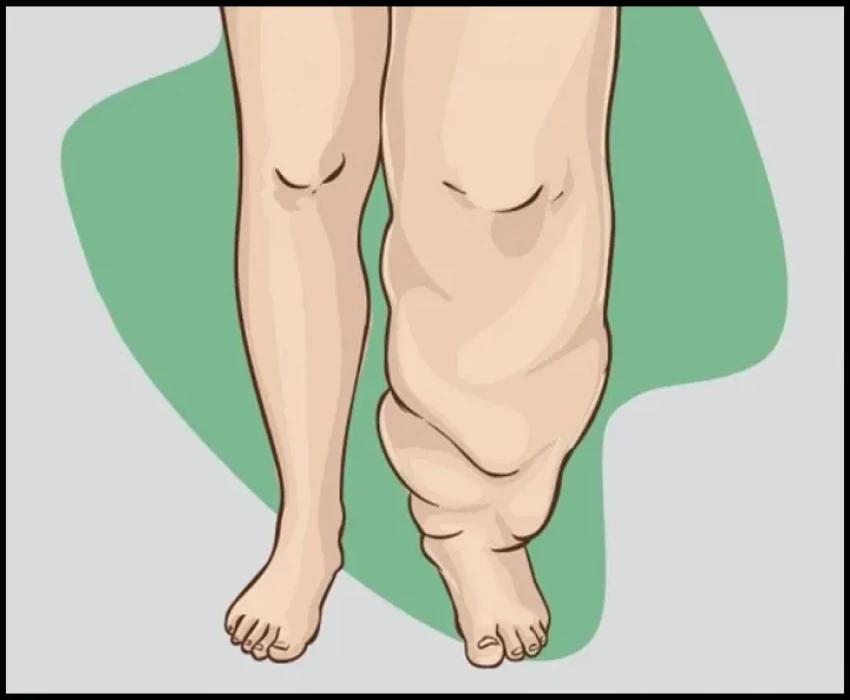
Lymphatic filariasis, commonly known as elephantiasis, is a painful and profoundly disfiguring disease. Lymphatic filariasis, considered globally as a neglected tropical disease (NTD), is a parasitic disease caused by microscopic, thread-like worms. The adult worms only live in the human lymph system. The lymph system maintains the body's fluid balance and fights infections.
There are three different filarial species that can cause lymphatic filariasis in humans. Most of the infections worldwide are caused by Wuchereria bancrofti. In Asia, the disease can also be caused by Brugia malayi and Brugia timori.
The infection spreads from person to person by mosquito bites. The adult worm lives in the human lymph vessels, mates, and produces millions of microscopic worms, also known as microfilariae. Microfilariae circulate in the person’s blood and infect the mosquito when it bites a person who is infected. Microfilariae grow and develop in the mosquito. When the mosquito bites another person, the larval worms pass from the mosquito into the human skin and travel to the lymph vessels. They grow into adult worms, a process that takes 6 months or more. An adult worm lives for about 5–7 years. The adult worms mate and release millions of microfilariae into the blood. People with microfilariae in their blood can serve as a source of infection to others.
A wide range of mosquitoes can transmit the parasite, depending on the geographic area. In Africa, the most common vector is Anopheles and in the Americas, it is Culex quinquefasciatus. Aedes and Mansonia can transmit the infection in the Pacific and Asia.
Many mosquito bites over several months to years are needed to get lymphatic filariasis. People living for a long time in tropical or sub-tropical areas where the disease is common are at the greatest risk for infection. Short-term tourists have a very low risk.
Programs to eliminate lymphatic filariasis are underway in more than 66 countries. These programs are reducing the transmission of the filarial parasites and decreasing the risk of infection for people living in or visiting these communities.


No Any Replies to “LYMPHATIC FILARIASIS”
Leave a Reply