With continually advancing knowledge and refinement in surgical techniques, the demand for facial rejuvenation and hair regeneration has now spread from celebrities to a common man keeping pace with the changing world of surgery to the mini or nanoworld.
Complete facial rejuvenation not only refers to surgery but also skin optimization, this is achieved via resurfacing to revitalize skin texture, refilling depressions with fillers and fat transfer and relaxing the muscles with Botox to smooth wrinkles. The surgical component entails releasing and redraping descended facial tissues back to their normal anatomical positions.
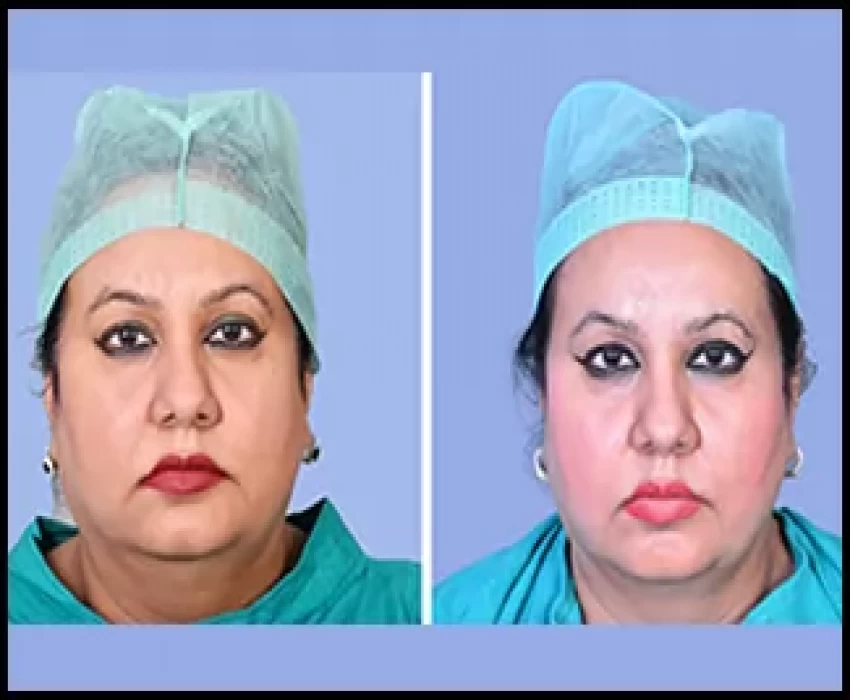
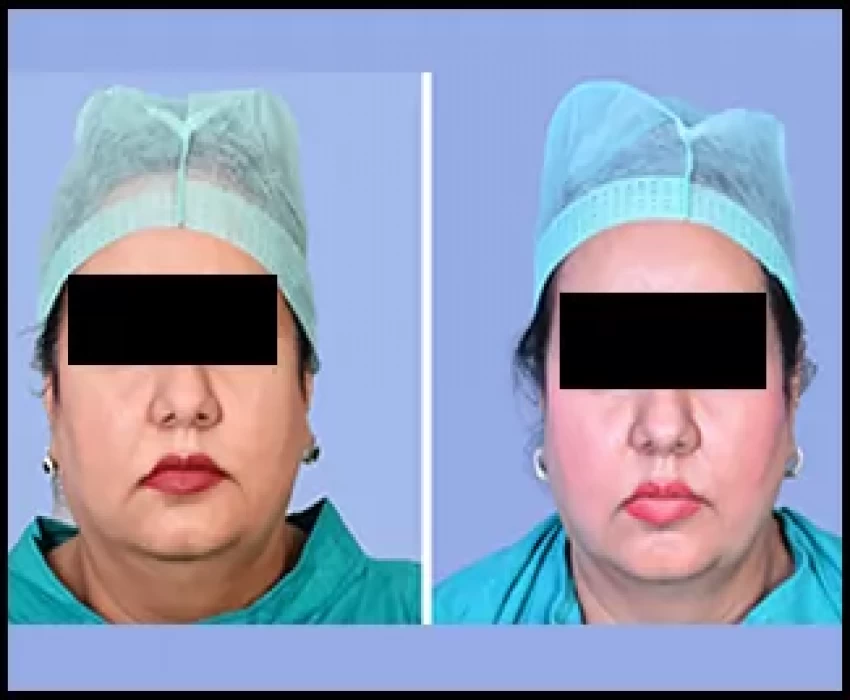
Facial rejuvenation aims to restore a youthful appearance to the face that can be achieved surgically and non-surgically. Surgical facial rejuvenation procedures are invasive procedures which includes facelifts, brow lifts, and so on. Non-surgical facial rejuvenation procedures are non-invasive procedures which includes chemical peels, derma fillers, etc.
Therefore, in order to correct the wrinkles, there are many procedures i.e. invasive & non-invasive procedures. Recently, there has been a growing trend for patients to pursue minimally invasive treatments which has reduced side effects and downtime to correct wrinkles and laxity. Polydioxanone threads and injectable platelet rich fibres being one of them.
Aesthetic procedures using absorbable PDO threads are an interesting alternative for facial rejuvenation. Different types of threads and techniques can be used depending on the patient’s needs. The great advantages of these techniques are the low morbidity and the low downtime from work. Proper training and knowledge of the different thread lifting techniques as well as adequate patient selection is crucial to be able to obtain good cosmetic results.
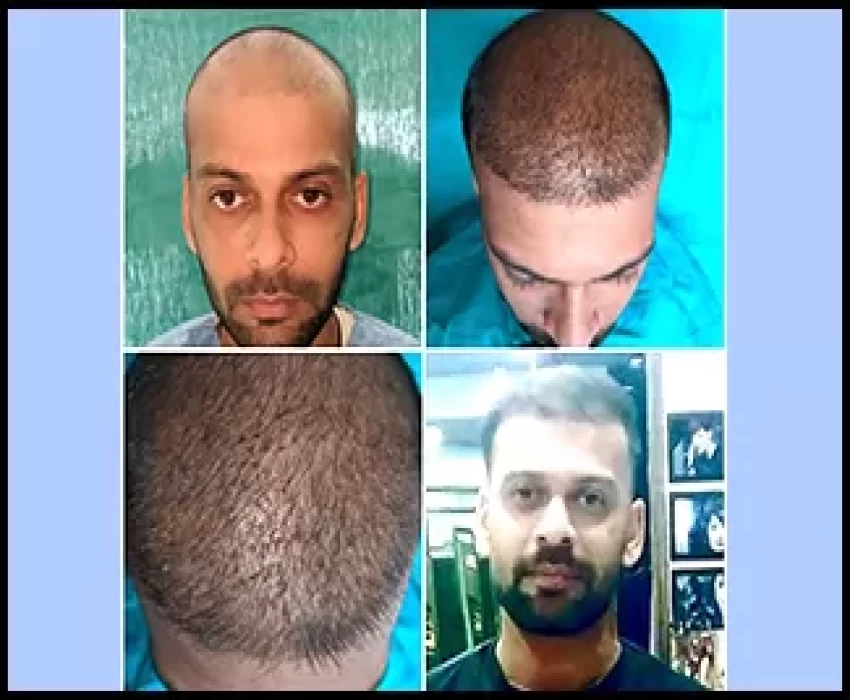
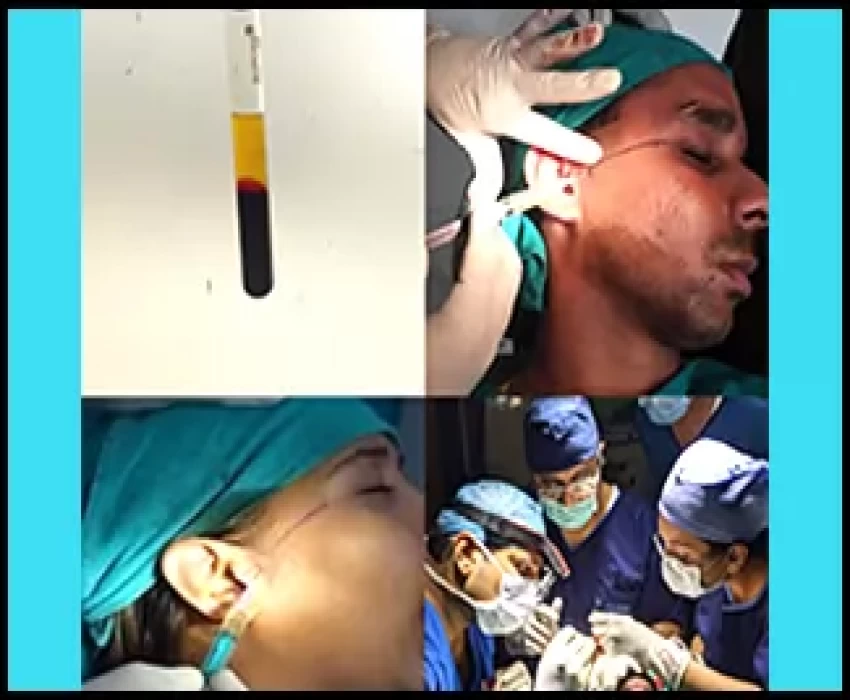
Hair transplantation is a surgical technique that removes hair follicles from one part of the body, called the 'donor site', to a bald or balding part of the body known as the 'recipient site'. The technique is primarily used to treat male pattern baldness. In this minimally invasive procedure, grafts containing hair follicles that are genetically resistant to balding (like the back of the head) are transplanted to the bald scalp. Hair transplantation can also be used to restore eyelashes, eyebrows, beard hair, chest hair, pubic hair and to fill in scars caused by accidents or surgery such as face-lifts and previous hair transplants. Hair transplantation differs from skin grafting in that grafts contain almost all of the epidermis and dermis surrounding the hair follicle, and many tiny grafts are transplanted rather than a single strip of skin.
Since hair naturally grows in groupings of 1 to 4 hairs, current techniques harvest and transplant hair "follicular units" in their natural groupings. Thus modern hair transplantation can achieve a natural appearance by mimicking original hair orientation. This hair transplant procedure is called follicular unit transplantation (FUT). Donor hair can be harvested in two different ways: strip harvesting, and follicular unit extraction (FUE).